Why a Working Prototype Doesn’t Mean Your Game Is Feasible
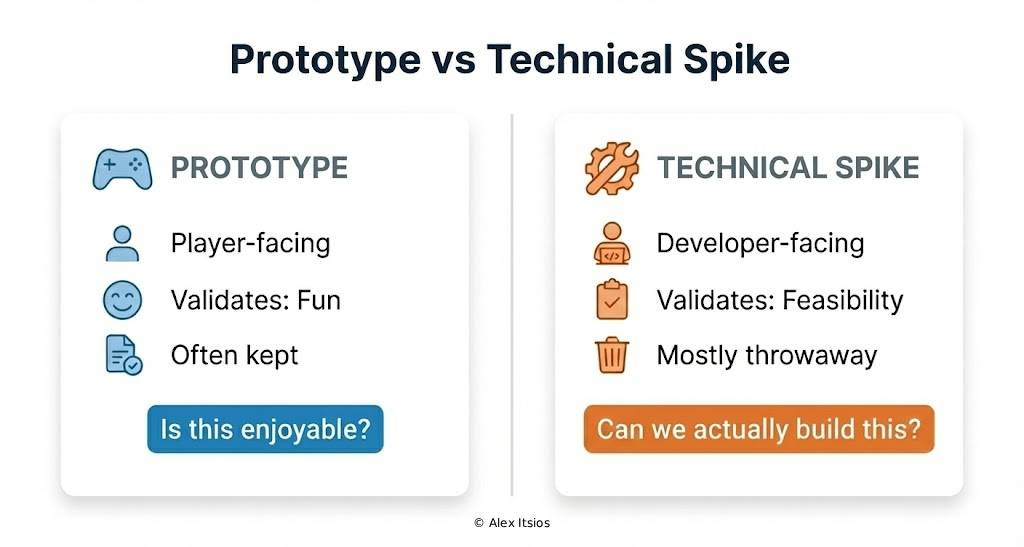
Prototypes validate fun. Technical spikes validate whether the game is feasible to be made.
You’ve prototyped your video game idea or even took a step further and made a vertical slice of your game. Despite that, your video game isn’t progressing as expected. You’re constantly hitting one barrier after the other, and you wonder why. Everyone’s been preaching the last few years that creating a prototype of your game is a smart move to verify if you can turn it into a full game. Unfortunately, creating a prototype doesn’t equate to feasibility, and it’s what most devs are missing.
By making a prototype, you’re verifying if the game is fun to play, but it doesn’t mean you can turn it into a functional game. That’s one of the most common reasons we, as devs, fail or constantly pivot. The real problem isn’t that your team isn’t prototyping enough, it’s that you don’t evaluate the risks first. By the way, this isn’t something new game developers struggle with; even seniors fall into this trap.
Being a lifelong learner, I solved this particular problem by applying technical spikes, something I’ve been using more and more recently in my solo projects. While this might sound like a new or niche concept, its roots come from Extreme Programming, one of the Agile methodologies. Its application is just as relevant today, from indie teams all the way up to AAA games.
In my personal projects, I used to start with the concept, create detailed documentation, then build a prototype or vertical slice to see if the game could be made. The benefits were obvious: if we couldn’t implement the prototype or it wasn’t fun enough, we’d iterate or stop development entirely. The issue was that further down the line, we would face technical barriers the team wasn’t aware of. The prototype answered “is this fun?”, but it didn’t answer “is this feasible to complete?”
This reminds me of one of my failed projects where I was the project lead a few years ago. We were trying to make a horror game for portfolio purposes. On paper, everything was going smoothly. The programmers had years of experience, and our documentation was clear and specific. Despite that, progress was minimal. Once we tried to fully implement the documentation, we ran into a series of technical issues that no one had anticipated, eventually leading to the project being abandoned entirely. The warning signs were there; we just never asked ourselves if they were feasible. That’s why in the last couple of years, I’ve been using technical spikes as early as the paper prototype phase to verify whether certain things are even possible.
The term originates from Extreme Programming and describes a time-boxed investigation designed to reduce technical risk. Unlike prototypes, which focus on player-facing value, technical spikes exist purely to generate knowledge.
What makes technical spikes different is that most of the work produced is throwaway. The code, assets, or setups exist only to answer a specific question. A lot of teams or individuals avoid doing this because it has no immediate gamer-facing value, and team leads or solo developers often assume these problems will be solved “later.” Trust me, they won’t. They’ll accumulate quietly over time. If you’re lucky, you’ll fail early. If you’re not, you’ll fail at a point where you’ve already invested months or years of time, energy, and money.
Technical spikes aren’t limited to programming either. They can be applied to art pipelines, animation workflows, content production, tooling, performance constraints, or even team capability. They are about exposing risk early, wherever that risk is.
For my newest projects, I always start with technical spikes to evaluate whether the game can realistically be made. In Parallel Pulse, for example, I initially created a 2D character sprite to evaluate the time and cost required. Very quickly, it became clear that this approach would be extremely time- and cost-intensive. Replicating this process across multiple characters and enemies made it obvious that I would never have the capital, time, or manpower to complete the game.
That spike didn’t give me a feature; it gave me a result. I pivoted and started exploring whether creating 3D characters in a similar style would be more efficient, since animations could be retargeted across characters. Because the game leans heavily toward an anime aesthetic, I’m now experimenting with 3D software specifically built to create anime-style characters quickly. Through this process, I also realized that quadruped enemies would be nearly impossible to support given the constraints. Without this spike, I would have discovered all of this much later, after committing fully to an unsustainable pipeline.
What surprised me most after adopting technical spikes wasn’t how often they killed ideas, but how often they saved them.